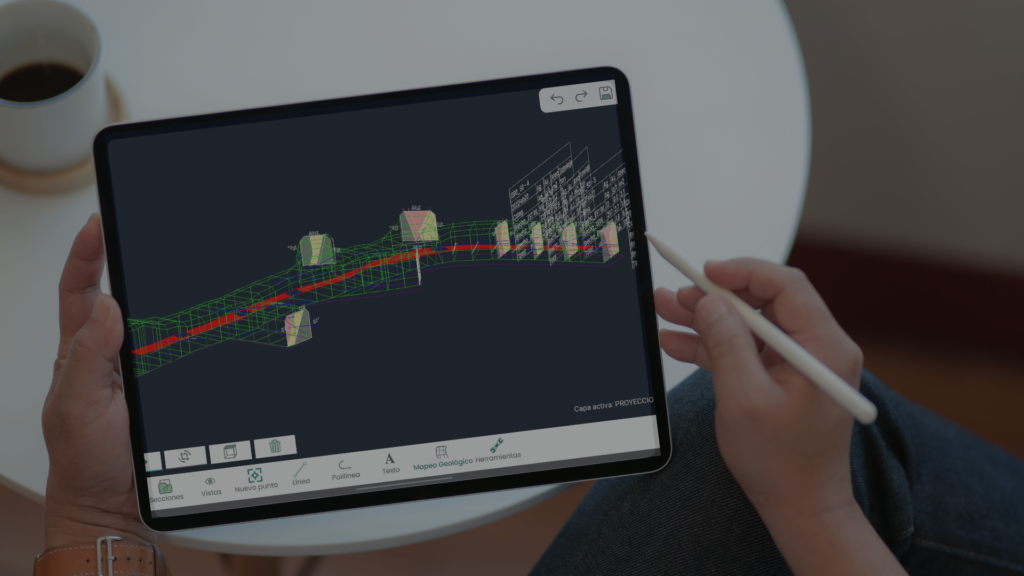
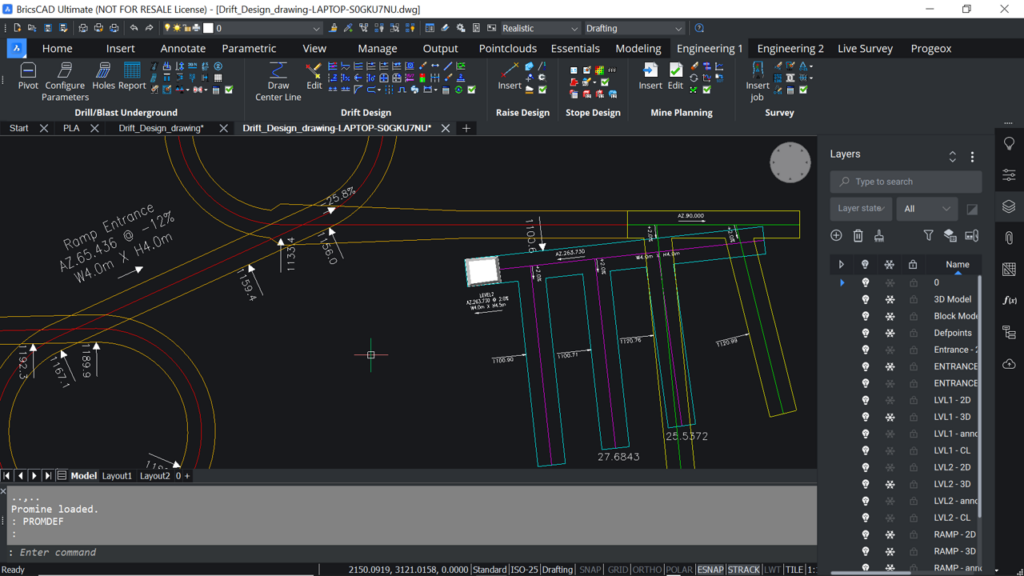
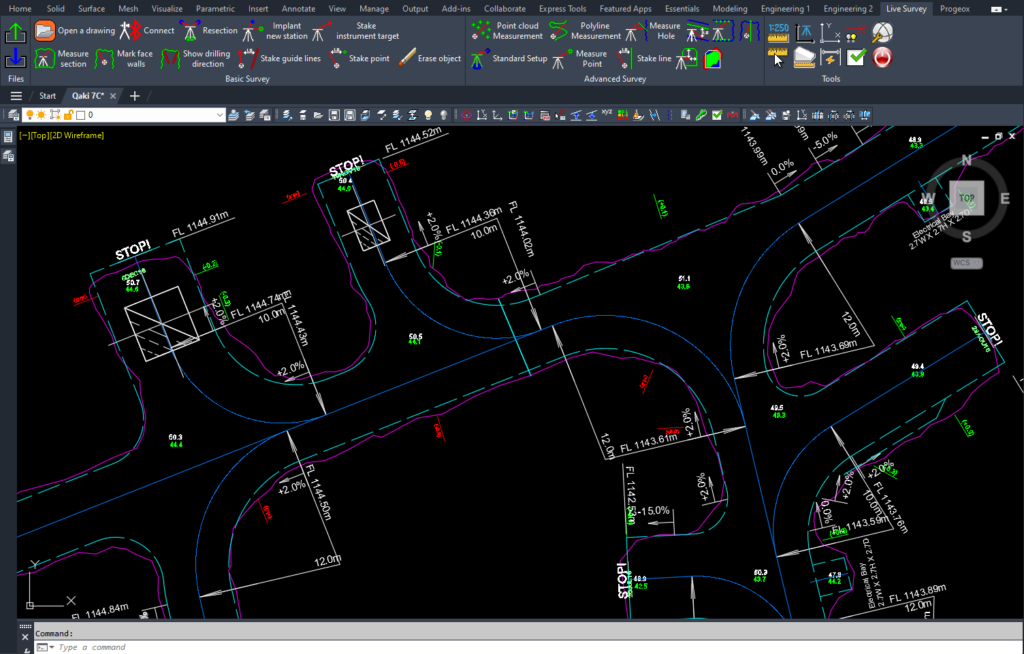
Simply put, digitization is the process of converting information into a digital format. In this format, information is organized into units that can then be addressed into binary data that computers and many devices with computing capabilities can then process.
With today’s wide array of electronic tools and devices, information can be easily gathered in a digitized format right at the source, thus facilitating future transfer, managing, storing and manipulation of the data. This was not the norm until very recently with the advancement of computer processing power. Prior to the wide use of computers and their affordability, all data relating to mining was recorded and stored in the traditional paper format, such as photographs, blueprints, handwritten field notes, sketches and drawings, paper core logs, etc. This form of analog data gathering and storage was time consuming, expensive, inefficient, and specially prone to being lost or damaged during the storage process.
Digitization of this historical data is of great importance to current and future engineers, geologist, and researchers who might not otherwise have access to long forgotten mining data. Digitizing information makes it easier to preserve, access, and share and occupies far less physical space than the original data. With tools such as scanners, OCR (Optical Character Recognition) software, digital cameras, etc., it is easier than ever to convert old data into a digital format. Digitization is becoming a strong trend in the mining sector, and it has been reported that 82% of the mining industry is willing to increase its investment in digital technology in the coming years in order to preserve its historical data (Ramírez, 2022).
The benefits of digitization in the mining industry are large but not always apparent at first. The process is slow and gradual as new ways of saving and accessing data must be learned and new tools have to be implemented. One of the major benefits of digitizing data is an improvement in productivity as less time is spent on saving and accessing data. Old data is readily available and is easily transferred without the need of physically having to look for it in some dark storage room. In addition to an increase in productivity, there are cost savings attributed to the digitization of data. Logistics costs are greatly reduced as it no longer is necessary to physically visit locations to research certain data or to courier data to people who are in need of it, add to that the savings in storage space that is no longer allocated to massive amounts of paper data that might or might not be useful again.
The digitization of data is a challenge that must be accepted by the mining industry as it moves into the future. As miners continue to look for mineral deposits, they will rely on data that was collected long ago but that was created long before the age of computers. The digitization of this data, along with current data being created will help to make sure that future generations will always have access to this data in an efficient manner and that data will no longer be easily lost with the passage of time.
Bibliography
Ramírez, O. (2022, 07 14). https://sptab.com/digitization-mining/. Retrieved from Stockholm Precision Tools: https://sptab.com/digitization-mining/